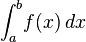From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Integral calculus)
This article is about the concept of integrals in calculus. For the set of numbers, see integer. For other uses, see Integral (disambiguation).
The term integral may also refer to the notion of antiderivative, a function F whose derivative is the given function ƒ. In this case, it is called an indefinite integral and is written: